There are two general categories of natural gas deposits. As the remains of animals microorganisms and plants begin to decompose they are gradually covered by layers of other materials.
 Natural Gas Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
Natural Gas Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
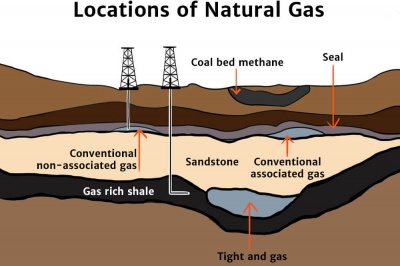
A type of natural gas found in coal deposits is called coalbed methane.
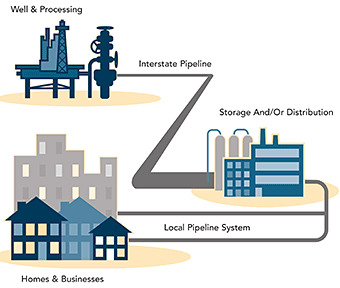
How we get natural gas. Natural gas also called fossil gas. Natural gas deposits are found on land and some are offshore and deep under the ocean floor. Sometimes just gas is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas mixture consisting primarily of methane but commonly including varying amounts of other higher alkanes and sometimes a small percentage of carbon dioxide nitrogen hydrogen sulfide or helium.
Conventional natural gas deposits are commonly found in association with oil reservoirs with the gas either mixed with the oil or buoyantly floating on top while unconventional deposits include sources like shale gas tight gas sandstone and coalbed methane. The natural gas deposits trapped deep within these rocks are hard to extract although recent technological advances in this field have made it possible to economically extract a large amount of natural gas from these sources. A number of different theories exist that suggest how natural gas is formed but the most prevalent theory suggests that natural gas forms underground as long as a string of specific and intense conditions is present.
Natural gas also occurs with deposits of crude oil and this natural gas is called associated natural gas. It is formed when layers of decomposing plant and animal matter are exposed to intense heat and. Deeper deposits formed at higher temperatures and under more pressure have more natural gas than oil.
Natural gas does not have to be formed deep underground however. Natural gas is extracted by drilling into the ground and using water to move the gas to the surface. Natural gas extraction involves using hydraulic pressure to make gas rise from deep wells to the surface.
Unconventional natural gas is mainly formed deep within the earth as can be seen illustrated in figure 3. Deposits of natural gas close to the earth s surface are usually dwarfed by nearby oil deposits. After the gas rises to the top it is necessary to separate it from other substances.
The deepest deposits can be made up of pure natural gas.