Usually the forward current of a normal led is considered as 20ma. When light emitting diode led is forward biased free electrons in the conduction band recombines with the holes in the valence band and releases energy in the form of light.
 Working Principles Of Leds Mobile Systems Tait Mobile Radio Bop Tauranga
Working Principles Of Leds Mobile Systems Tait Mobile Radio Bop Tauranga
In the led the recombination of charge carrier takes place.
Light emitting diode operation. A light emitting diode led is known to be one of the best optoelectronic devices out of the lot. The device is capable of emitting a fairly narrow bandwidth of visible or invisible light when its internal diode junction attains a forward electric current or voltage. The quantum theory says that when the electron comes down from the higher energy level to the lower energy level then the energy emits from the photon.
Construction of light emitting diode the construction of light emitting diode is so much simple it is made by depositing the three layers of semiconductor material on a substrate. Light emitting diodes have a higher luminous efficacy how efficiently electricity is converted to visible light than incandescents a 60 watt incandescent bulb can generate between 750 900 lumens but you can get the same output from a led bulb using only 6 8 watts. An led or a light emitting diode is semiconductor device that emits light due to electroluminescence effect.
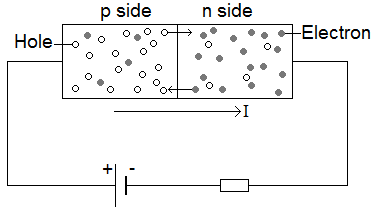
Recall from chapter 1 that these free electrons are in the conduction band and at a higher energy than the holes in the valence band. The basic operation of the light emitting diode led is as follows. A light emitting diode led is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it.
The visible lights that an led emits are usually orange red yellow or green. When the device is forward biased electrons cross the pn junction from the n type material and recombine with holes in the p type material. An led is basically a pn junction diode which emits light when forward biased.
Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes releasing energy in the form of photons the color of the light corresponding to the energy of the photons is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. The electron from the n side and the hole from the p side are combined and gives the energy in the form of heat and light. These three semiconductor material layers are made three regions which are called a p type region which is top one active region which is middle one and n type region which is bottom one.
Light emitting diodes are almost everywhere. A light emitting diode led is an optical semiconductor device that emits light when voltage is applied. The led is a pn junction diode which emits light when an electric current passes through it in the forward direction.
Light emitting diode led definition. The resistance value of the series resistor can be calculated using the below formula. The working principle of the light emitting diode is based on the quantum theory.
Light emitting diode functions well when it is connected in series with the resistance as a result the forward current required by the led is provided by supply voltage across the combination. In other words led is an optical semiconductor device that converts electrical energy into light energy. The photon energy is equal to the energy gap between these two energy levels.